Prevention
Core task
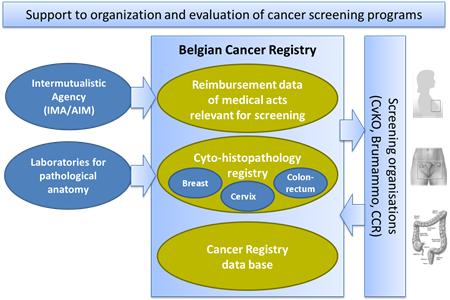
To set up a central cyto-histopathological data base (CHP) for an effective organization and quality evaluation of cancer screening programs.
Creation of CHP registries
All laboratories for Pathological Anatomy are legally obliged since 2010 to transmit all the results of breast, cervical and colorectal samples to the Belgian Cancer Registry (BCR).
Completing CHPs with nomenclature data base from the Intermutualistic Agency: reimbursement data of medical acts that are relevant for the detection, monitoring and treatment of breast, colon and cervical cancer.
Objectives
- Exclusion lists: Compiled by BCR, consist of all persons for which a screening examination is not required for the next invitation round in order to send invitations more focused, which reduces costs.
- Registration of follow-up: Any abnormal screening test needs a follow-up in order to verify whether a cancer (precursor) has been detected by the screening test. After all, an abnormal screening test does not indicate with certainty cancer. The databases of SKR allow to ascertain whether the patient with an abnormal screening result was referred to a doctor and contain the result of the follow-up study.
- Analysis of screen-detected and interval cancers: Interval cancers are diagnosed after a negative screening within a time period equal to the screening interval.
- Quality indicators: Calculated to closely monitor the quality of the screening programs to identify issues that need improvement.
- Screening-related research projects: The CHP registries offer a wide variety of possibilities for research projects.
Collaborations with screening organisations
Top